GEODRILL takes pride in its highly experienced and versatile team, particularly in geophysical survey projects.
Our key personnel bring extensive expertise in project management, geophysical services, and equipment rental—individually or combined.
We are committed to delivering high-resolution survey results with precision. Data can be processed and interpreted on-site or at our Riyadh-based data centre , with reporting available in various professional formats.
At GEODRILL , we continually strive to advance survey methodologies and provide tailored solutions to even the most complex challenges.




RANGE OF GEOPHYSICAL SURVEYS
01. MASW (Multi-channel Analysis of Surface Waves)
02. Electrical Resistivity Tomography
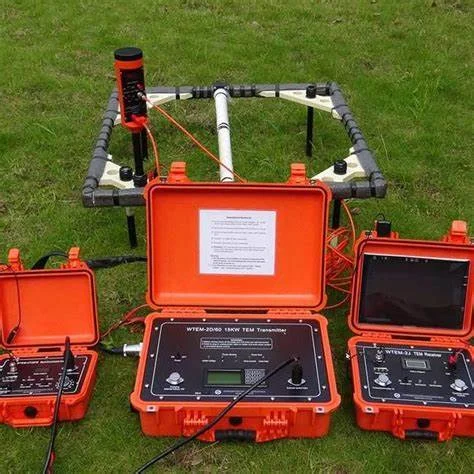
03.Microgravity Surveys 04. Electromagnetism: EM34
05. Ground Penetrating Radar
06. Radio Detection / Utilities detection
07. Vertical Electric Sounding
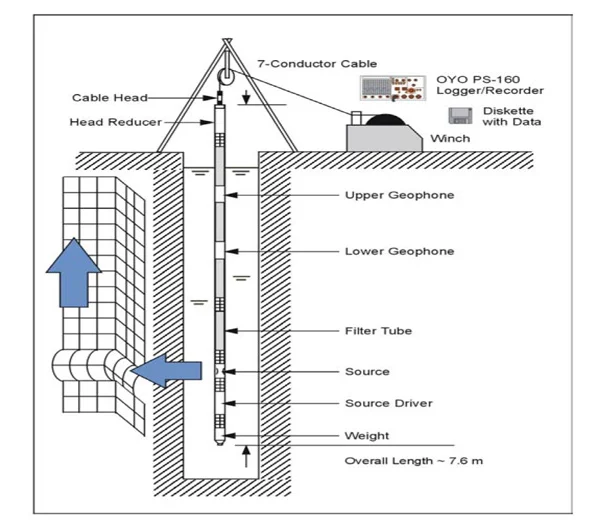
08. Cross-hole seismic
09. Down-hole seismic
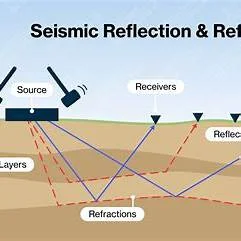
10. Refraction seismic Reflection seismic
11. Magnetic survey
12. Gravity exploration (Macro)
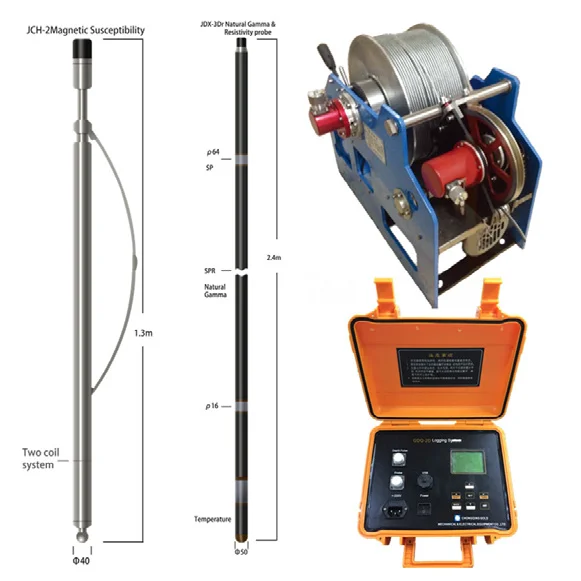
13. Suspension logging
14. Vertical Electrical Tomography (VET)
15. Resistivity, temperature logging
16. Magnetic survey
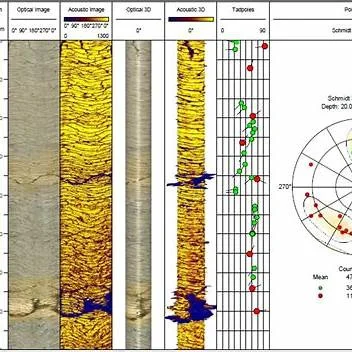
17. Acoustic Tele viewer & Camera Logging






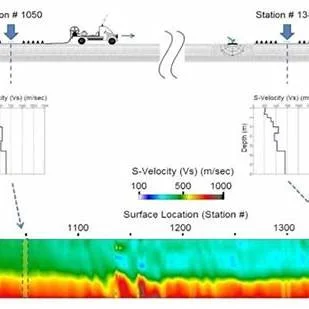
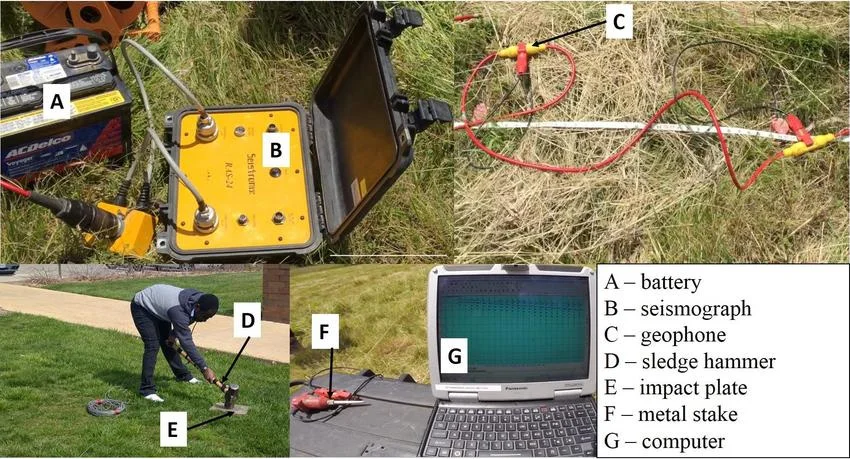
MASW
(Multi-channel Analysis of Surface Waves)
Applications of MASW
MASW (Multi-channel Analysis of Surface Waves) is a non-invasive geophysical
technique used to evaluate subsurface shear-wave velocity profiles by analysing
surface wave dispersion.
It is widely applied in geotechnical and geophysical investigations due to its
efficiency, accuracy, and ability to characterize shallow subsurface conditions
without the need for drilling.
MASW measures the propagation of surface (Rayleigh) waves generated by a
controlled seismic source and recorded by an array of geophones.
The data is processed to develop 1D, 2D, or 3D velocity models, which reflect soil
stiffness and layering—crucial for engineering design and site characterization.
Applications of MASW
01. Site Classification (e.g., for seismic hazard analysis as per NEHRP or Eurocode
02. Determination of Vs30 (average shear-wave velocity in the upper 30 meters)
03. Detection of soft layers or weak zones and cavities
04. Soil liquefaction potential studies
05. Compaction control and ground improvement
06. Verification Subsurface profiling for infrastructure design
(e.g., roads, dams, buildings)
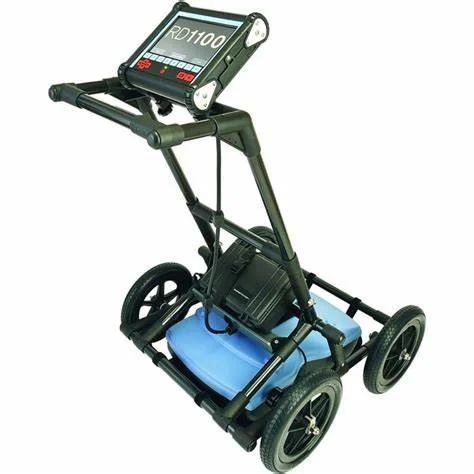
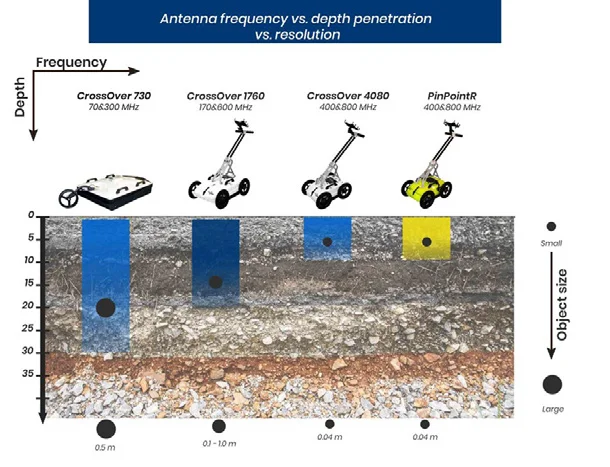
GROUND PENETRATION RADAR SURVEYS
Ground Penetrating Radar, also known as Geo radar or GPR, uses Radar
technology to obtain a continuous profile of the subsurface.
The Georama is of immense application in areas requiring high resolution
information of relatively shallow subsurface.
Depth of penetration of radar signal depends on the frequency used and
material properties.
The application of GPR technology includes:
01. Detection of underground utilities(pipes & Cables)
02. Detection of Soil Bed rock interface, shallow geological investigations.
03. Detection of subsurface cavities voids & fractures
(Structures Building Bridges and Dams
04. Detection of contaminations in ground for environmental studies.
05. Mineral Exploration using cracks & fractures studies.
06. Water table detections.
07. Road Investigations (Layer thickness &Subsidence
08. Honeycomb Weathering & Voids detection in Concrete pillars & walls.


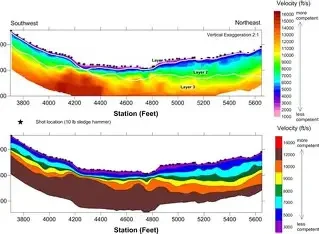
SEISMIC REFRACTION
Seismic technique is one of the most developed geophysical techniques,
providing vital information on subsurface, crucial for most of the engineering
projects.
GEODRILL specializes in Seismic Refraction surveys, routinely carried out for
assessment of subsurface conditions prior to engineering projects.
The seismic refraction surveys
are used to determine the following:
01. Bed Rock profile, rock quality & depth.
02. Thickness of over burden weathered
03. Slope Stability Study guides.
04. Pipeline Route Studies for soil/rock properties layer.
05. Fractures & weak zones determinations.
06. Topography of ground water & aquifers
07. Rippability assessment in Mines.
08. Slope Stability Study guides.
09. Pipeline Route Studies for soil/rock properties.
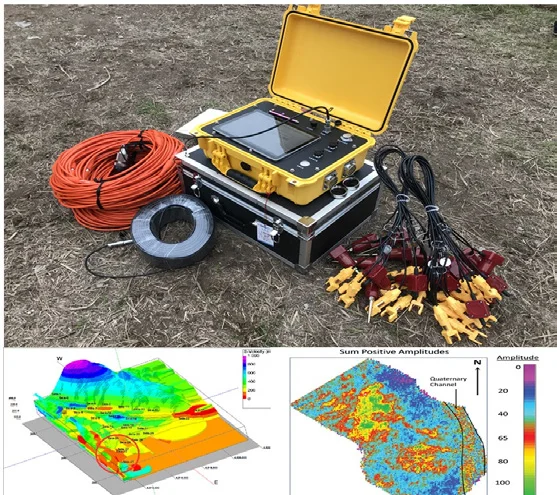


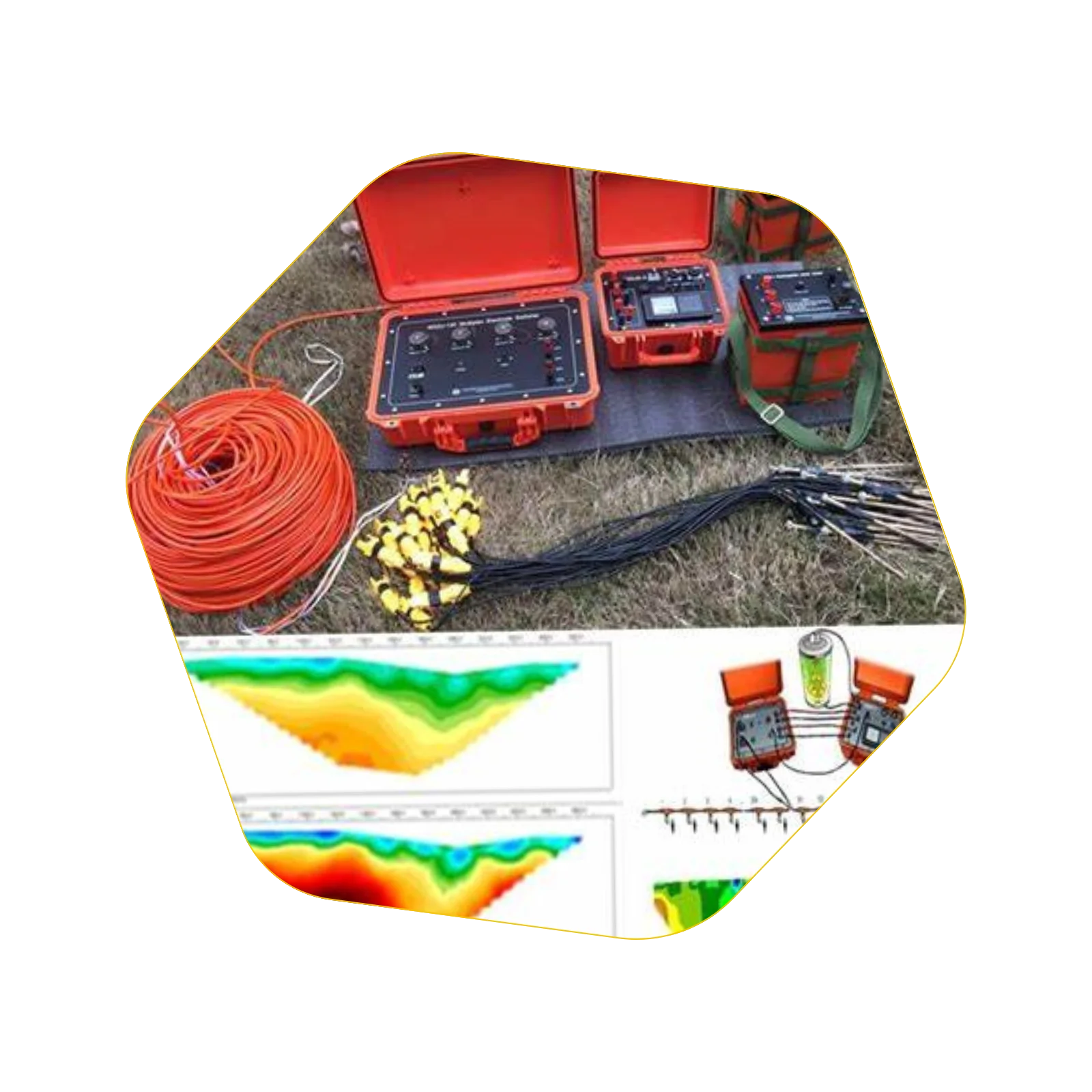
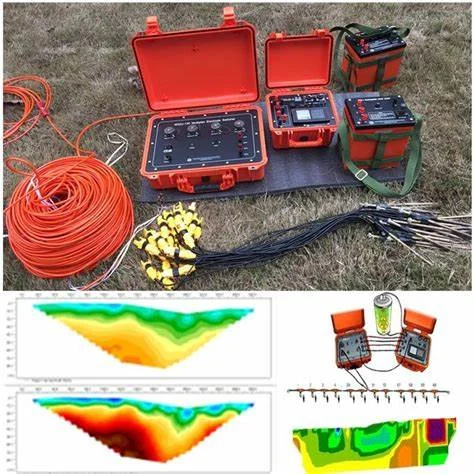
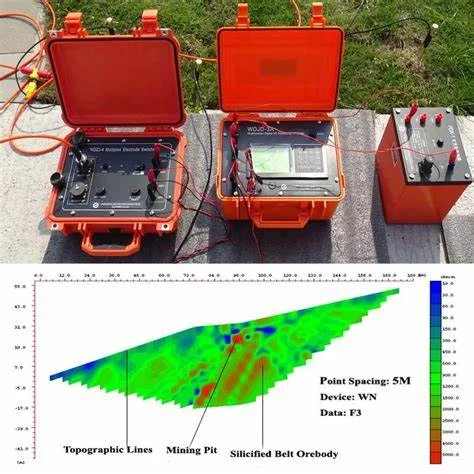
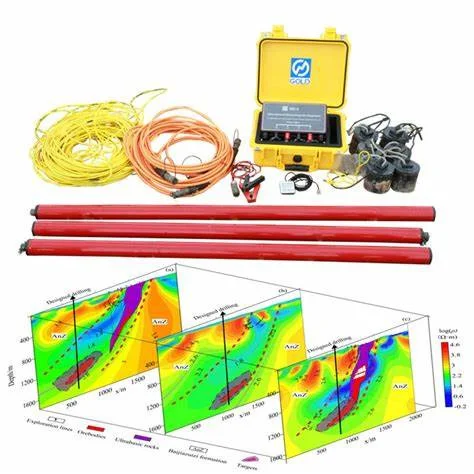
ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY SURVEYS
(Sounding & Tomography) :
The electrical methods, used for measurement of subsurface resistivity, involve
passing an electrical current into the ground using two electrodes, and measuring
resultant potential using two potential electrodes.
Resistivity sounding involves gradually increasing the spacing between the current
and/or potential electrodes to obtain deeper penetration.
Under profiling , The electrode spacing is kept constant and the entire arrangement
is moved along profile lines, to obtain lateral variation in subsurface resistivity.
The Electrical surveys are used in civil engineering, water resources, mining and
environmental projects to:
01. Landfills Studies.
02. Dam structure analysis.
03. Mineral prospecting
04. Bed Rock quality & Depth measurements.
05. Determine underground water resources.
06. Stratigraphic studies for soil/rock depths.
07. Contaminating of Oil/fuel detections.
08. Determine sinkholes, cavities & fractures.



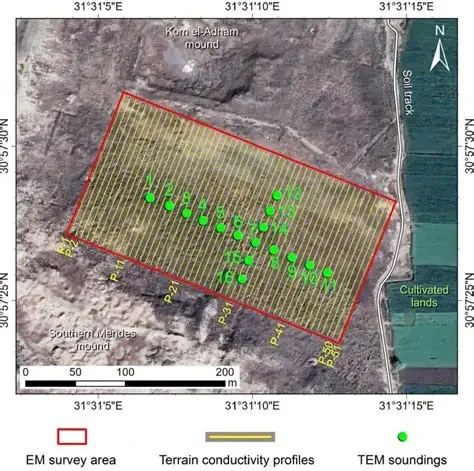
EMI (Electromagnetic Induction) :
Electromagnetic Induction,(EMI) is the most widely used technology for locating
buried services and is very effective in most soil types.
With EMI, you can locate and trace a facility, as well as estimate its depth.
Electromagnetic Induction consists of two steps. First, a transmitter is used to
transfer an alternating electrical current to the pipe or wire to be located.
Next, a receiver is used to analyze the transmitted signal and localize the position
and depth of the facility.
The transmitter can transfer the signal to the facility either by a direct connection, or by inducing a signal .
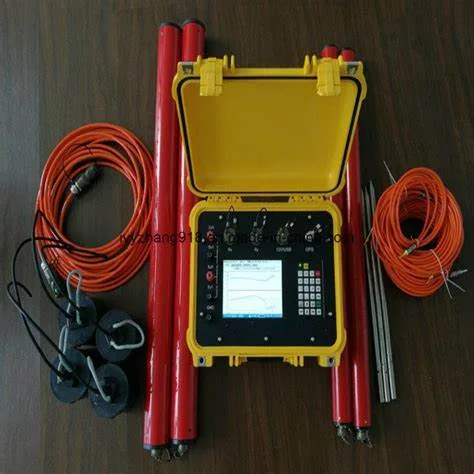
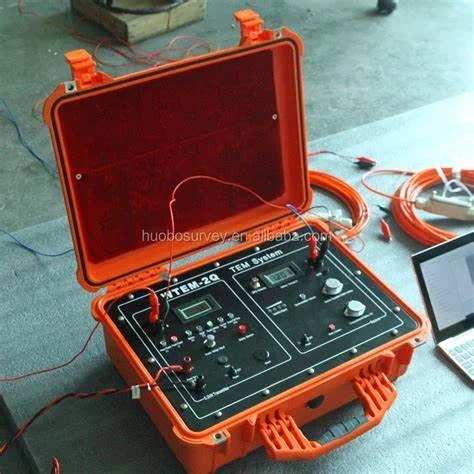


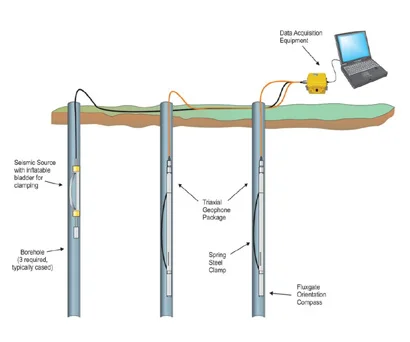
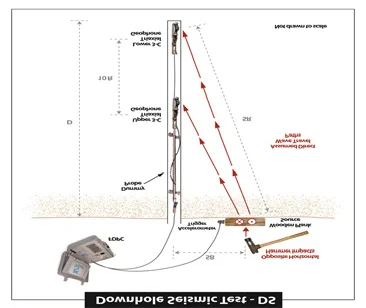
CROSS HOLE & DOWN HOLE SEISMIC SURVEYS:
The Crosshole seismic surveys are used to derive information on the elastic
properties of materials between two or more boreholes by measuring travel time of
seismic energy-One hole is used as shot hole, and another hole as receiver hole, and
travel time from source to receiver is measured at different depths.
Using P & S wave travel times, dynamic moduli are calculated, For down hole, single
hole is used for seismic wave’s velocity calculations.



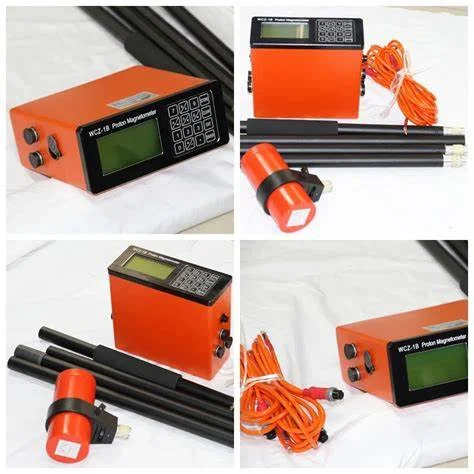
MAGNETIC SURVEYS:
The Magnetics surveys are rapid and efficient.
The device magnetometers can be used to detect buried ferrous metal objects
(tanks or drums) or bedrock features with contrasting magnetite content.
Detection depends on the amount of magnetic material present and its distance
from the sensor.
The hidden structures can be detected at burial estimated from magnetometer data
collected using the gradient method.
It is applied for the following applications;
01. Preliminary Survey in Rose compass Certification Site surveys.
02. Detection of underground buried tanks & drums.
03. Geological mapping
04. Mineral Explorations & fractures detections.
05. Archeological studies.
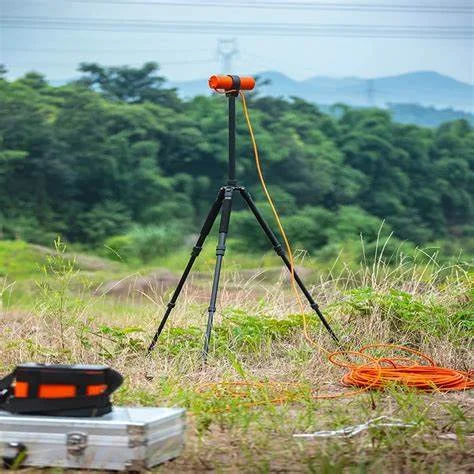



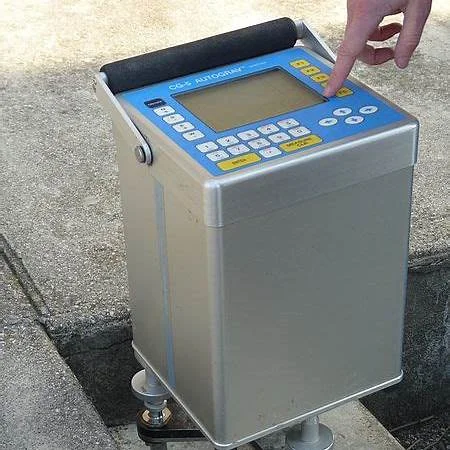
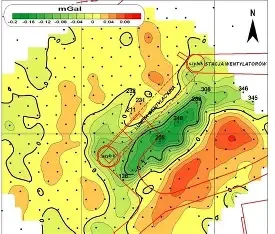
MICROGRAVITY SURVEYS:
The gravity Surveys can provide useful information where other methods don’t
work. For example, gravity may be used to map bedrock topography under a
land fil, where seismic refraction is limited.
Gravity survey is used for following purposes;
01.Mapping of Lateral Lithological Changes.
02. Mineral Exploration (Sulphide, copper, Iron, zinc deposits
03. Bed Rock topography under landfills
04. Underground Cavities & Voids detections.
05. Detection & Mapping of large metallic mineral deposits.
06. Locating contacts between geological units of different
mass & density


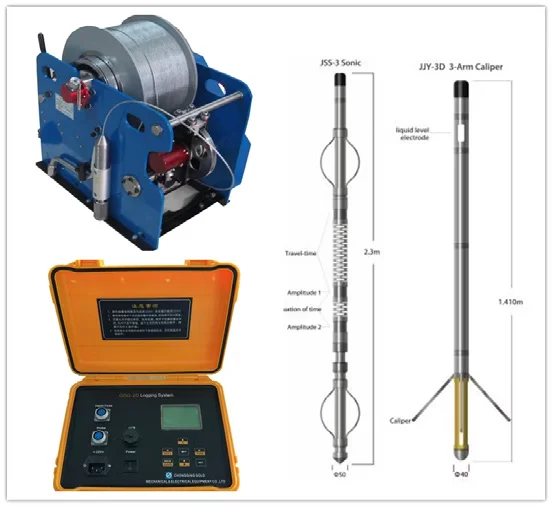
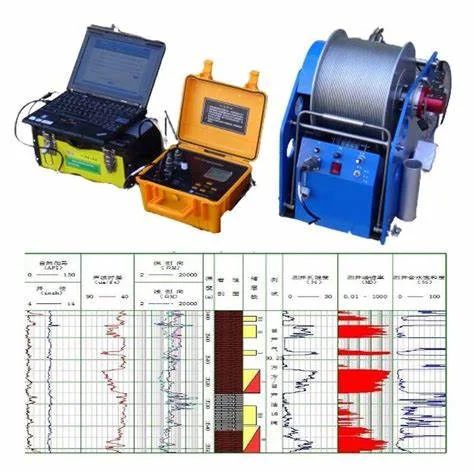
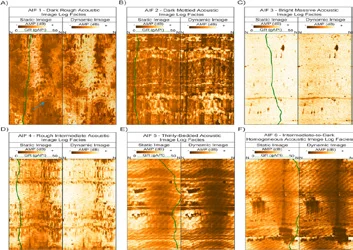
Optical and Acoustic Logging
The Optical and Acoustic Televiewer provides continuous logs of oriented, high
resolution unwrapped video images of borehole walls. Further processing allows for
the computation and display of standard information on fractures and other
geological features.
The optical televiewer is fully downhole digital and can be run on any standard
wireline.
THE PURPOSE OF THE OPTICAL IMAGING TOOL IS TO PROVIDE DETAILED,
ORIENTED, STRUCTURAL INFORMATION. POSSIBLE APPLICATIONS ARE :
01. Fracture detection and evaluation
02. Detection of thin beds
03. Determination of bedding dip
04. Lithological interpretation




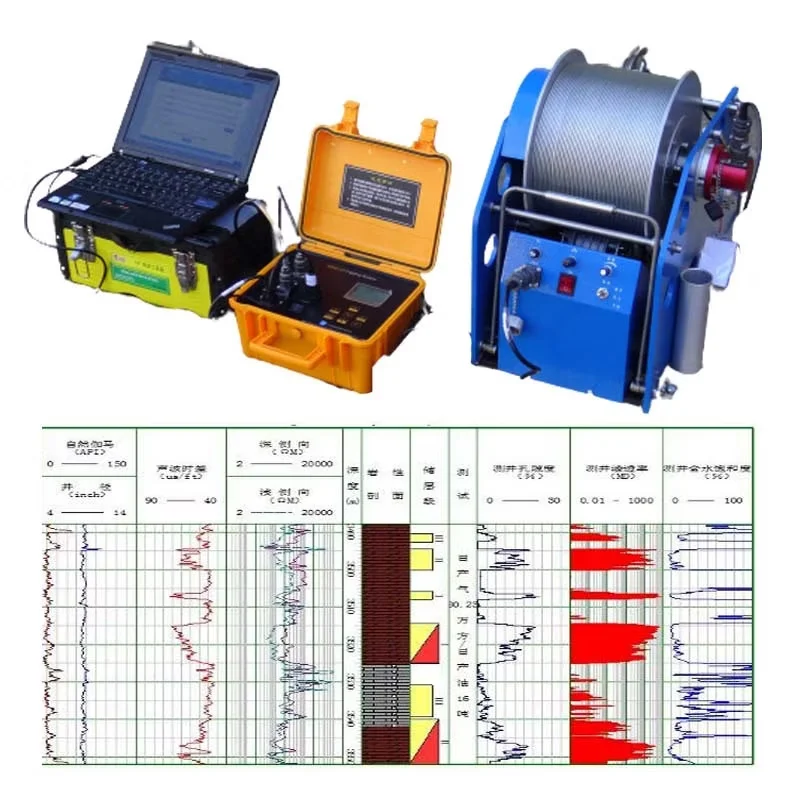
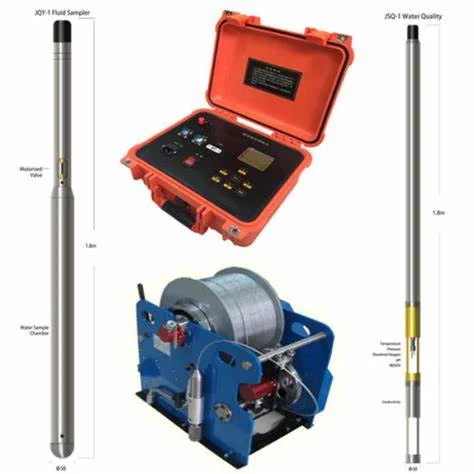
Suspension logging
Suspension logging is a geophysical borehole logging method used to measure
subsurface formations’ properties by lowering a probe (or sonde) suspended on
a cable into a borehole.
It is commonly used in hydrogeological, geotechnical, and mineral exploration
projects to obtain continuous data about the borehole’s depth, lithology, and
structural integrity.
Applications
01. Hydrogeology: Identifying aquifer characteristics, groundwater flow, and
contamination levels.
02. Geotechnical Engineering: Assessing soil and rock stability for
construction projects.
03. Mining & Exploration: Mapping ore bodies and determining mineral
concentrations.
04. Oil & Gas: Evaluating reservoir properties and formation integrity